In part 2, we will go through many code snippets from the two apps, showing REST and GraphQL approaches one below the other. They will not contain information that is in my opinion obsolete for this article like initializing Google Maps, styles and some template parts.
In part 1 of GraphQL vs REST, I went through some basic concepts and differences between the two approaches.
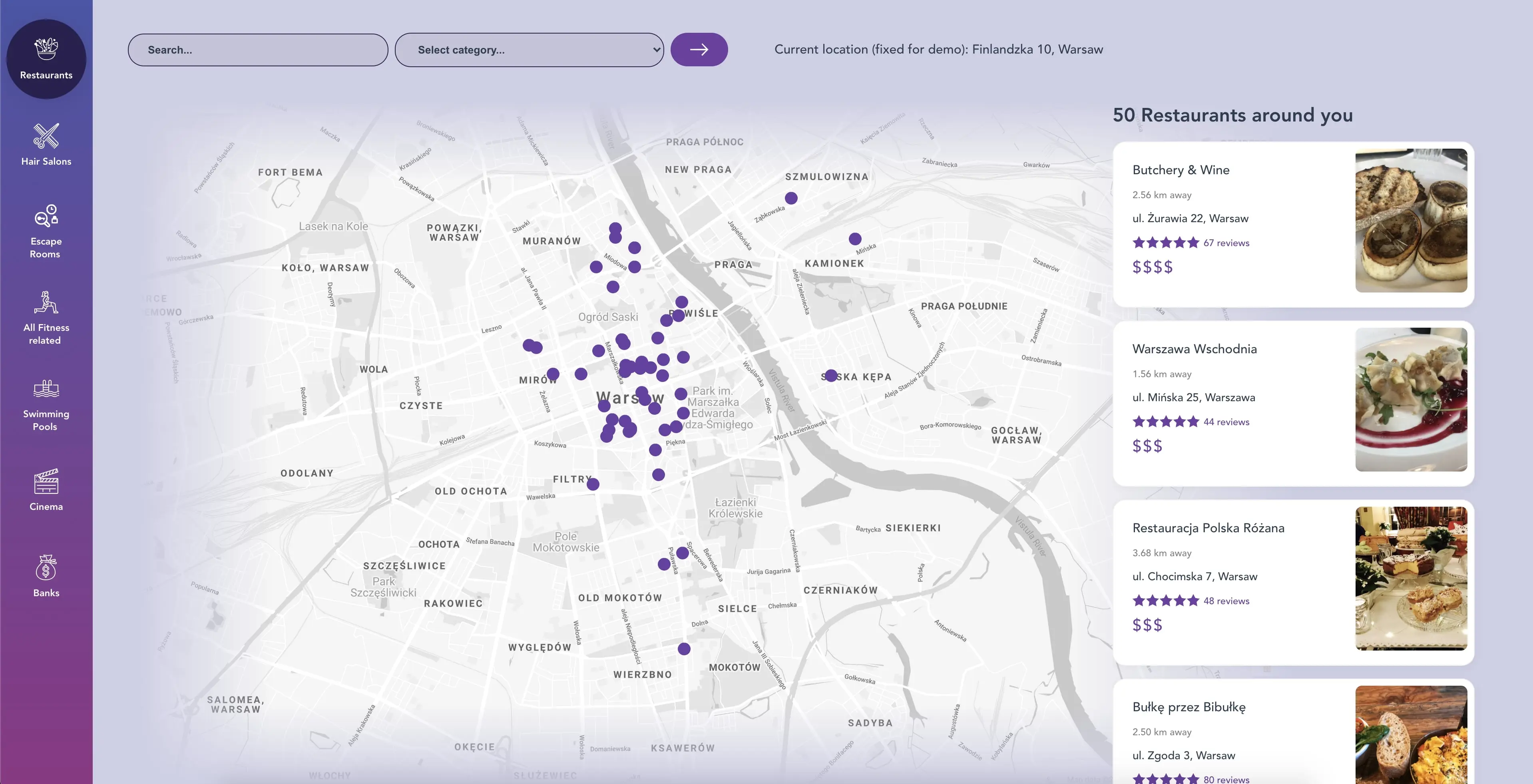
Main configuration
In Rest, I’ve decided to use Vuex.
In GraphQL, main library to keep state is VueApollo.
REST
// main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
import '@/config/axios.config';
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
router,
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
GraphQL
import Vue from 'vue';
import App from './App.vue';
import router from './router';
import VueApollo from 'vue-apollo';
import { apolloClient } from './config/apollo.config';
Vue.config.productionTip = false
Vue.use(VueApollo)
const apolloProvider = new VueApollo({
defaultClient: apolloClient,
defaultOptions: {
$query: {
loadingKey: 'loading',
fetchPolicy: 'cache-and-network'
}
}
})
new Vue({
router,
apolloProvider,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')Other configuration
In REST, let’s use Axios for making API requests. We will use axios later in Vuex store. For now, let’s only initialize default state.
In GraphQL, Apollo provides a lot of boilerplate, but I also import InMemoryCache and typeDefs. To have some default data in the beginning I write data to cache. During creating new Apollo Client, it’s important to remember that even without mutations in the project, empty resolvers are needed.
REST
// config/axios.config.js
import axios from 'axios';
axios.defaults.baseURL = process.env.VUE_APP_API_BASE_URL;
axios.defaults.headers.common['Authorization'] = `Bearer ${process.env.VUE_APP_YELP_API_KEY}`;
// part of store/index.js to show where empty data is initialized
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import axios from 'axios';
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
results: [],
activeCategory: {},
loading: false,
activeMarker: null,
categories: []
},
...
GraphQL
// config/apollo.config.js
import { ApolloClient } from 'apollo-client'
import { createHttpLink } from 'apollo-link-http'
import { InMemoryCache } from 'apollo-cache-inmemory'
import { setContext } from 'apollo-link-context';
import { typeDefs } from '@/graphql/typeDefs';
// HTTP connection to the API
const httpLink = createHttpLink({
// You should use an absolute URL here
uri: process.env.VUE_APP_API_BASE_URL
})
const authLink = setContext((_, { headers }) => {
// get the authentication token from local storage if it exists
// return the headers to the context so httpLink can read them
return {
headers: {
...headers,
authorization: `Bearer ${process.env.VUE_APP_YELP_API_KEY}`,
'Accept-Language': `en_US`
}
}
});
// Cache implementation
const cache = new InMemoryCache()
cache.writeData({
data: {
search: {
business: [],
__typename: 'Search'
},
activeCategory: {
__typename: 'ActiveCategory'
},
loading: false,
activeMarker: null,
center: {
lat: 52.237022,
lng: 21.050440,
__typename: 'MapCenter'
},
zoom: 12,
categories: []
},
});
// Create the apollo client
export const apolloClient = new ApolloClient({
link: authLink.concat(httpLink),
cache,
typeDefs,
resolvers: {}
})Fetching initial results
In REST, I do it by dispatching an action on mounted in App.vue
In GraphQL, there are two ways of doing it. Here, I went for the ApolloQuery component with a v-slot approach. This gave me easy access to result data, loading state and query to refetch data later. Take note of notifyOnNetworkStatusChange set to true.
Another way to do it is to use apollo key on the same level as mounted and specify the query there.
REST
<script>
// part of App.vue
export default {
...
mounted() {
this.$store.dispatch('getInitialResults');
this.$store.dispatch('getCategories');
}
}
</script>
GraphQL
// part of App.vue
<template>
...
<ApolloQuery
:query="GET_RESULTS"
:notifyOnNetworkStatusChange="true"
>
<template v-slot="{ result: { data, loading }, query }">
<AppNav @search="handleSearch($event, query)" />
<div class="content"></div>
</template>
</ApolloQuery>
...
</template>Making requests
In REST, the requests to API can go either from components or store, like in my example. Since actions are asynchronous in Vuex, this is the best place to fetch data.
In GraphQL, I’ve created three files that are responsible for specifying queries, one for all type definitions, but the requests for e.g. results go from App.vue through ApolloQuery component.
REST
// store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import axios from 'axios';
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
results: [],
activeCategory: {},
loading: false,
activeMarker: null,
categories: []
},
mutations: {...},
actions: {
async getCategoryResults({commit}, payload) {
commit('setCategoryResultsMutation', []);
commit('setActiveCategoryMutation', payload);
commit('setLoading', true);
const {data: { businesses }} = await axios.get(`businesses/search?categories=${payload.name}&latitude=52.237022&longitude=21.050440&limit=50&radius=15000&sort_by=best_match`);
commit('setCategoryResultsMutation', businesses);
commit('setLoading', false);
},
async getCategories({commit}) {
commit('setLoading', true);
const {data: { categories }} = await axios.get(`categories`);
commit('setCategoriesListMutation', categories);
commit('setLoading', false);
},
async getInitialResults({commit}) {
commit('setLoading', true);
const {data: { businesses }} = await axios.get(`businesses/search?latitude=52.237022&longitude=21.050440&limit=50&radius=15000&sort_by=best_match`);
}
}
GraphQL
// graphql/categories.query.js
export const GET_CATEGORIES = gql`
query AllCategoriesQuery {
categories {
total
category {
title
alias
}
}
}
`
// graphql/results.query.js
export const GET_RESULTS = gql`
query GetResults($term: String, $category: String) {
search (
term: $term,
categories: $category,
limit: 50
latitude: 52.237022,
longitude: 21.050440,
radius: 15000
) @connection(key: "search") {
total
business {
name
distance
location {
address1
city
}
url
rating
review_count
price
photos
coordinates {
latitude
longitude
}
}
}
}
`
// graphql/local.query.js
export const GET_ZOOM = gql`
{
zoom @client
}
`
export const GET_CENTER = gql`
{
center @client {
lat
lng
}
}
`
// graphql/typeDefs.js
export const typeDefs = gql`
type MapCenter {
lat: String!
lng: String!
}
type Category {
title: String!
alias: String!
}
type Categories {
total: Int!
category: Category!
}
type BusinessLocation {
address1: String!
city: String!
}
type Business {
name: String!
distance: String!
url: String!
rating: String
review_count: String
price: String
photos: [String]
location: BusinessLocation
}
type Search {
total: Int!
business: Business!
}
`;Handling loading
In REST, I use a global Vuex loading flag that I change during API calls and I directly access it through $store object. Since the app is small, one such key is enough.
In GraphQL it proved to be more difficult. When I tried to use the apollo key in script and refetch of data, my $apollo.queries.search.loading was always false during 2nd and later fetches. Because of that, I changed the approach to ApolloQuery component and used loading in App.vue, which is later passed to Results component as a prop.
REST
// part of components/Results.vue
<div
class="results__wrapper"
v-else-if="$store.state.loading"
>
<h2 class="results__wrapper-loading">
Loading...
</h2>
</div>
// store/index.js
actions: {
async getQueryResults({commit}, {input, category}) {
commit('setCategoryResultsMutation', []);
commit('setLoading', true);
const {data: { businesses }} = await axios.get(`businesses/search?term=${input}&categories=${category}&latitude=52.237022&longitude=21.050440&limit=50&radius=15000&sort_by=best_match`);
commit('setCategoryResultsMutation', businesses);
commit('setLoading', false);
}
}
GraphQL
// part of components/Results.vue
<div
class="results__wrapper"
v-else-if="loading"
>
<h2 class="results__wrapper-loading">
Loading...
</h2>
</div>
// part of App.vue
<ApolloQuery
:query="GET_RESULTS"
:notifyOnNetworkStatusChange="true"
>
<template v-slot="{ result: { data, loading }, isLoading, query }">
<AppNav @search="handleSearch($event, query)" />
<div class="content">
...
<Results
:results="data && data.search && data.search.business"
:loading="loading"
/>
</div>
</template>
</ApolloQuery>
<script>
methods: {
handleSearch({ term, category }, query) {
query.refetch({term, category});
}
}
</script>Summary
These are the most important parts of the app and main differences between the two apps. To see the whole project and compare, please visit my GitHub repositories. You can clone the project, register API keys on Yelp and Google Maps and see it working:
Github repo for GraphQL approach
Check out part 3!