The carbon credit market is critical in terms of corporate sustainability. Yet, it faces significant challenges, with transparency and trust being the most important. For large enterprises committed to reducing their carbon footprint, these issues are critical barriers to achieving their ESG goals. How is blockchain a solution that promises to tackle these most pressing issues?
Key considerations:
- Blockchain technology addresses critical issues in the carbon credit market, such as transparency, trust, double counting, fraud, and verification difficulties, by creating a secure, transparent, and immutable ledger of transactions.
- Enterprises face challenges in the carbon credit market and in scaling greentech solutions, including lack of transparency, regulatory uncertainty, high implementation costs, and technological complexities.
- 10Clouds’ Super Registry case study demonstrates blockchain's potential to enhance trust and transparency in the carbon credit market.
- Blockchain enhances greentech by improving data collection and analysis, tracking renewable energy generation and consumption, facilitating decentralized energy grids, and providing transparency in supply chains.
- Challenges of large enterprises include scalability and interoperability of blockchain solutions, regulatory uncertainty, implementation costs and complexity, and the need for specialized knowledge and expertise.
Carbon credits are permits that allow companies or countries to emit a certain amount of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases. One credit equals one ton of CO2. These credits can be traded on markets, providing an economic incentive for reducing emissions.
Unfortunately, the current carbon credit system is fraught with problems such as double counting, fraud, and a lack of transparency, making it difficult for enterprises to verify the authenticity of their sustainability efforts.
Blockchain technology, known for its role in cryptocurrencies, offers a compelling solution to these challenges. By creating a secure, transparent, and immutable ledger of transactions, it can provide a single source of truth for the carbon credit market, among other benefits.
In this article, we examine the current state of the carbon credit market, the unique benefits blockchain offers, and the integration of greentech solutions for large enterprises.
The Current State of Carbon Credits and Greentech for Enterprises
The traditional carbon credit market is marred by the lack of transparency and verification, regulatory uncertainty, price volatility, data traceability issues, and reputational risks.
Scaling greentech solutions presents another set of challenges. Despite the clear benefits of adopting green technologies, enterprises face obstacles in implementation, from high upfront costs to technological complexities.
Moreover, the absence of a standardized framework for evaluating the impact of these technologies complicates their integration into existing business models.
In this challenging environment, enterprises have clear needs.
- Firstly, they must meet their ESG goals, which requires reliable and verifiable sustainability efforts. This is not just about reducing carbon footprints but also about demonstrating these efforts transparently to stakeholders, including investors, customers, and regulatory bodies.
- Secondly, as regulatory pressures increase, finding efficient and reliable carbon offsetting solutions becomes paramount.
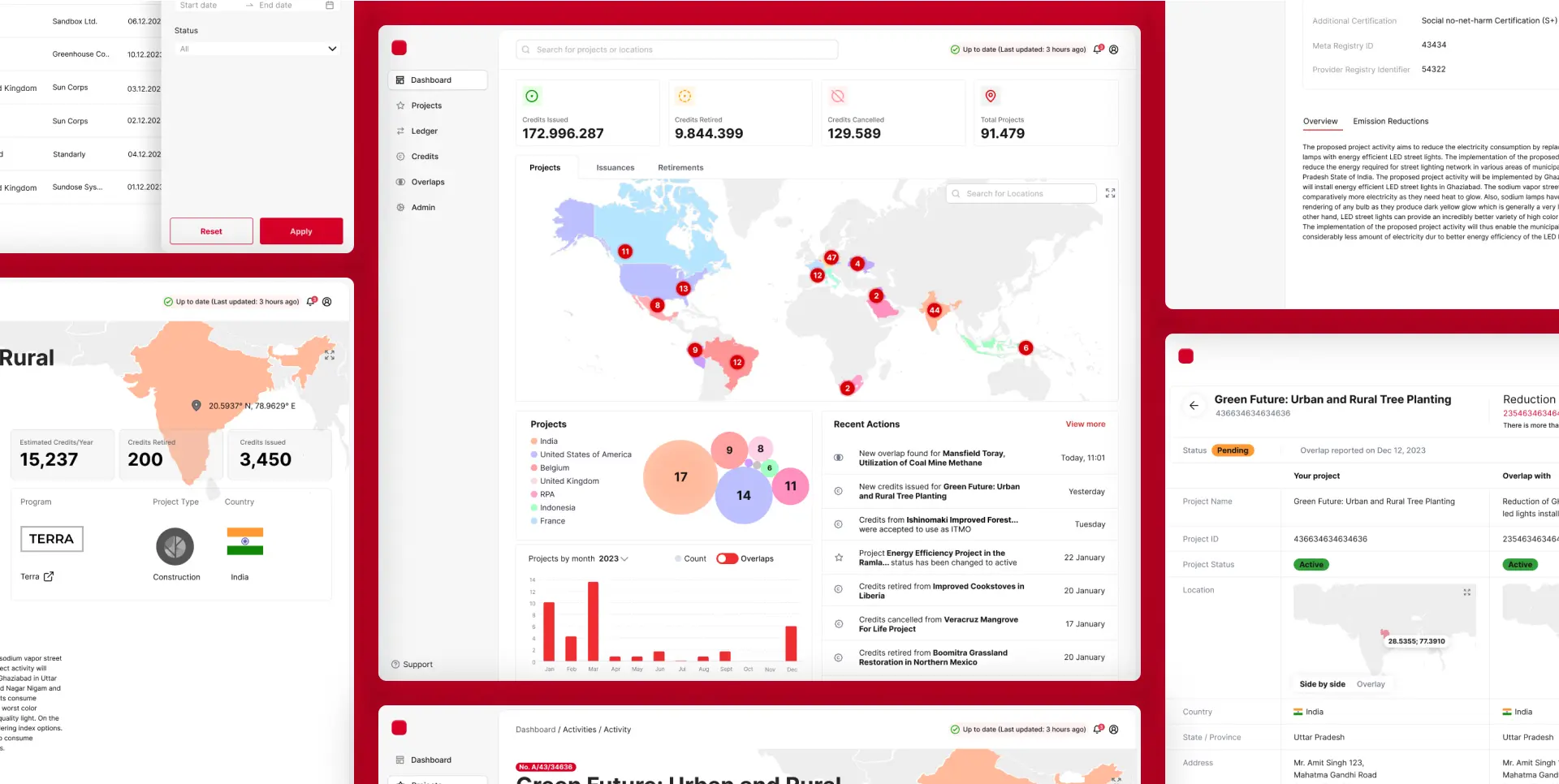
The Super Registry case study - a glimpse into the greentech solutions
The Super Registry project 10Clouds helped deliver offers a glimpse into how blockchain technology can address some of these challenges. By creating a super-registry for carbon credits, the project aimed to provide a single, trustworthy source of information, enhancing trust and transparency in the market.
Moreover, the simple and reliable user interface, despite the underlying blockchain complexity, facilitated broader adoption and usability, showing a way forward for integrating greentech solutions into the carbon credit market.
Read our Super Registry case study to learn what challenges we tackled.
Blockchain's Potential in Carbon Credit Markets
Blockchain’s potential to revolutionize the carbon credit sector lies in its core characteristics: transparency, immutability, and efficiency. These features address the fundamental challenges that have long plagued the carbon credit system.
Enhanced transparency and traceability
One of the most significant advantages of blockchain is its ability to provide a transparent and traceable record of transactions. In the context of carbon credits, this means every credit's journey can be tracked from issuance to retirement, ensuring that each credit is only used once and its environmental impact is clear. This level of transparency is crucial for building trust among market participants and stakeholders.
Immutable record-keeping for verifiable transactions
Blockchain's immutable ledger ensures that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted. This immutability guarantees the integrity of carbon credit transactions, making it easier for enterprises to prove their sustainability efforts and comply with regulatory requirements.
Improved security and reduced risk of fraud
The decentralized nature of blockchain significantly reduces the risk of fraud and manipulation. By distributing the ledger across multiple nodes, blockchain makes it nearly impossible for any single entity to alter transaction records, thereby enhancing the security of the carbon credit market.
Automated smart contracts for streamlined transactions
Blockchain enables the use of smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. In the carbon credit market, smart contracts can automate the issuance, trading, and retirement of credits, streamlining processes and reducing the potential for human error.
Tokenization of carbon credits for greater liquidity
Blockchain facilitates the tokenization of carbon credits, turning them into digital assets that can be easily traded. This increases market liquidity, making it easier for enterprises to buy and sell credits in response to their changing emissions and sustainability goals.

Specific Applications of Blockchain in Super Registry
The Super Registry case study exemplifies blockchain's potential in creating a secure and transparent carbon credit registry. Here are some of the specific use cases this project utilized.
Facilitating peer-to-peer carbon credit trading
By enabling direct trading between parties without the need for intermediaries, blockchain could reduce transaction costs and increase market efficiency.
Enabling real-time monitoring and verification
Blockchain supports real-time monitoring and verification of carbon offsetting projects in Super Registry, ensuring that they deliver the promised environmental benefits and that credits are issued accordingly.
Improving efficiency of carbon credit issuance and retirement
Through automation and streamlined processes, blockchain can make the issuance and retirement of carbon credits more efficient, reducing administrative burdens and costs.
Successful Web3 Greentech Projects
KlimaDAO
KlimaDAO is pioneering a shift in the carbon credit landscape by leveraging blockchain technology to foster transparency and efficiency. Operating as a decentralized autonomous organization, it empowers its community through token-based governance, enabling stakeholders to actively participate in shaping the platform's direction. At the heart of its mission is the KLIMA token, which facilitates the tokenization and retirement of carbon credits, thereby enhancing market liquidity and integrity. By addressing the inherent inefficiencies and opacity of traditional carbon markets, KlimaDAO strives to accelerate global climate finance, ultimately driving increased investment into impactful climate action initiatives.
dClimate
dClimate is a decentralized marketplace for climate data, built on blockchain technology, that aims to bring transparency and accessibility to the often opaque world of environmental information. It connects climate data providers with users, such as researchers, insurers, and businesses, enabling them to access reliable and verifiable climate datasets. By leveraging blockchain, dClimate ensures the integrity and immutability of this data, fostering trust and facilitating the development of innovative climate-related solutions.
Powerledger
Powerledger is an Australian technology company that has developed a blockchain-based platform for peer-to-peer energy trading and renewable energy tracking. Their technology allows for decentralized energy marketplaces, enabling consumers and producers of renewable energy to directly trade electricity with each other, cutting out intermediaries and promoting the use of distributed renewable energy sources. They also provide solutions for renewable energy certificate (REC) trading and grid management.
Sunified
Sunified is a platform that leverages blockchain technology to facilitate investment in solar energy projects. It aims to democratize access to solar investments by tokenizing solar assets, allowing individuals and institutions to participate in and benefit from renewable energy production. By providing transparent and verifiable data on solar project performance, Sunified increases trust and streamlines the investment process, ultimately accelerating the adoption of solar energy.
OpenSC
OpenSC is a platform developed by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and BCG Digital Ventures that uses blockchain technology to track the environmental and social impact of products throughout their supply chains, transforming global food systems. It aims to bring transparency and accountability to supply chains, allowing consumers and businesses to make informed choices about the products they buy and sell. By providing verifiable data on the origins and journey of products, OpenSC promotes sustainable and ethical sourcing practices.
Greentech Integration and Synergies
The synergy between green technologies and blockchain offers a powerful tool for enterprises to enhance their sustainability efforts, improve efficiency, and foster transparency across their operations. Let's explore how greentech benefits from blockchain and examine some successful integrations.
Improved data collection and analysis
Blockchain can significantly enhance the way data is collected, stored, and analyzed in environmental projects. By providing a secure and immutable platform, it ensures the integrity of environmental data, whether it's related to carbon emissions, renewable energy generation, or resource consumption. This reliable data is crucial for making informed decisions and demonstrating real impact.
Enhanced tracking of renewable energy generation and consumption
Blockchain technology enables the precise tracking of renewable energy generation and consumption. Through tokenization, units of renewable energy can be digitally created, bought, sold, and retired, providing clear evidence of an enterprise's green energy use. This not only supports corporate sustainability goals but also promotes the growth of renewable energy markets.
Facilitating decentralized energy grids and carbon offsetting initiatives
Blockchain's ability to support decentralized networks can revolutionize energy grids, allowing for more efficient distribution and consumption of renewable energy. Moreover, it can streamline carbon offsetting initiatives by connecting projects directly with funders, ensuring transparency and trust in the offsetting process.
Transparency in supply chains for sustainable products
Blockchain can provide unparalleled transparency in supply chains, enabling companies to prove the sustainability of their products from raw materials to finished goods. This visibility is essential for meeting consumer demand for ethical and environmentally friendly products.
Other examples include blockchain-enabled renewable energy platforms that allow consumers to buy, sell, or trade renewable energy credits directly, bypassing traditional energy markets. Such platforms not only promote the use of renewable energy but also empower consumers to take an active role in the energy transition.
Challenges and Considerations for Large Enterprises
While the integration of greentech and blockchain holds great promise, it's not without its challenges. Scalability, interoperability between different blockchain platforms, and the evolving regulatory landscape are significant considerations. Enterprises must navigate these challenges carefully, ensuring that their blockchain initiatives are scalable, compliant, and capable of integrating with existing systems.
As large enterprises explore the integration of blockchain technology and greentech solutions into their operations, they encounter a unique set of challenges and considerations. These hurdles are not just technical but also strategic, requiring careful planning and execution to overcome.
Scalability and interoperability
One of the primary challenges is scalability. Blockchain technology, while promising, can sometimes struggle to handle the vast transaction volumes and data throughput required by large enterprises. Ensuring that blockchain solutions can scale effectively to meet the needs of a large organization is crucial. Additionally, interoperability between different blockchain platforms and existing enterprise systems poses a significant challenge. Enterprises often operate a complex web of legacy systems, and integrating new blockchain solutions without disrupting existing operations requires careful planning and execution.
Regulatory uncertainty
The regulatory landscape for blockchain and carbon credits is still evolving. Enterprises must navigate this uncertainty, ensuring that their blockchain initiatives comply with current regulations while also being adaptable to future changes. This includes understanding the legal implications of tokenizing carbon credits and navigating the complexities of international regulations when operating across borders.
Implementation costs and complexity
Implementing blockchain technology and greentech solutions can be costly and complex. The initial investment in technology, alongside the need for specialized knowledge and skills, can be significant barriers. Enterprises must evaluate the costs and benefits carefully, considering not just the immediate financial outlay but also the long-term savings and efficiencies that these technologies can bring.
Team and expertise
The need for specialized knowledge and expertise cannot be overstated. Blockchain technology and greentech solutions are highly specialized fields, and enterprises must either develop this expertise in-house or seek external partners. This includes not just technical skills but also strategic and regulatory knowledge to navigate the challenges mentioned above.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of integrating blockchain and greentech solutions are significant. Enterprises that successfully navigate these considerations can not only enhance their sustainability efforts but also gain a competitive edge in the market.
The key is to approach these challenges with a clear strategy, ensuring that the solutions implemented are scalable, compliant, and integrated seamlessly with existing operations.
Recommendations for enterprises
Conduct thorough Due Diligence
Before implementing blockchain solutions, enterprises should conduct a detailed due diligence process. This includes evaluating the technology's scalability, security, and compatibility with existing systems, as well as assessing the credibility and track record of technology providers.
Prioritize transparency and security
In all blockchain and greentech projects, transparency and security should be top priorities. Enterprises should implement robust security measures to protect data and transactions and ensure that their sustainability efforts are transparently reported to stakeholders.
Collaborate with experienced blockchain developers and consultants
Given the complexity of blockchain technology and the specialized knowledge required, enterprises should seek to collaborate with experienced developers and consultants. Experts such as 10Clouds can provide valuable insights into the best practices for implementing blockchain solutions and navigating regulatory challenges.
Stay informed about regulatory developments
The regulatory landscape for blockchain, carbon credits, and greentech is continually evolving. Enterprises should stay informed about regulatory changes and developments to ensure ongoing compliance and adapt their strategies as necessary.

Conclusion
The future of carbon credits and greentech in the enterprise sector is intrinsically linked to blockchain technology. As we move forward, the integration of these technologies offers a path to more transparent, efficient, and reliable sustainability efforts. Enterprises that embrace these innovations and adapt to the evolving landscape will be well-positioned to lead in the transition to a more sustainable and low-carbon economy.
As we look ahead, the landscape of carbon credits, greentech, and blockchain is ripe with opportunities for innovation and growth. The emergence of AI and IoT, the development of standardized protocols for carbon credit tokenization, and the growth of decentralized marketplaces are just a few of the trends that promise to shape the future of this space. For enterprises, the path forward involves embracing these technologies, conducting thorough due diligence, prioritizing transparency and security, and staying informed about regulatory developments.


